Google introduced a new feature for its AI model Gemini 2.5, which allows highlighting and analyzing parts of images using ordinary text queries. Users can now interact with the model in natural language and receive responses that consider complex queries, such as “person with an umbrella” or “everyone who is not sitting.” Gemini recognizes not only clear objects but also abstract concepts like “clutter” or “damage,” and can also find elements based on text in the image.
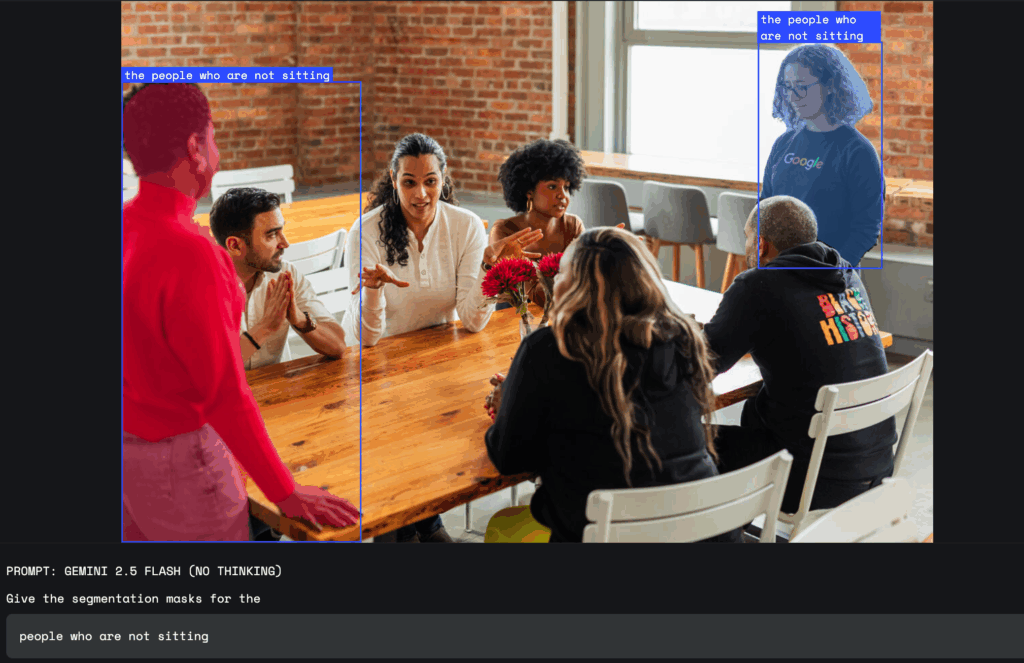
The feature supports multilingual queries and can provide captions for objects in other languages. Users receive results in the form of coordinates of the selected area, pixel masks, and captions, allowing quick identification of the desired part of the image. There is no need to use separate tools or models, as everything is processed by the Gemini model itself.
Developers have access to the new capability through the Gemini API. Google recommends using the “gemini-2.5-flash” model and setting the “thinkingBudget” parameter to zero for instant responses. Initial testing can be conducted in Google AI Studio or through Python Colab.
The feature will be useful for designers, who can now highlight details in photos with simple commands, such as “highlight the building’s shadow.” In the field of occupational safety, Gemini will help identify violations, such as “all people on the construction site without helmets.” In insurance, this capability allows for automatic marking of damaged buildings on aerial photographs, saving time during damage assessment.



