Surfshark reports draw attention to how much personal information modern generative AI chatbots collect. Experts from the company analyzed ten of the most popular applications, including ChatGPT, Meta AI, Google Gemini, Copilot, DeepSeek, Poe, Claude, Jasper, Perplexity, and Pi, and found that each model accumulates a certain amount of user data.
The absolute leader in terms of collected information is the Meta AI model, which records thirty-two out of thirty-five possible types of data. The list even includes sensitive categories such as financial information, health data, and personal beliefs. Both Meta AI and Copilot use data related to user identification to display third-party ads, with Meta AI potentially involving up to twenty-four types of data for this purpose.
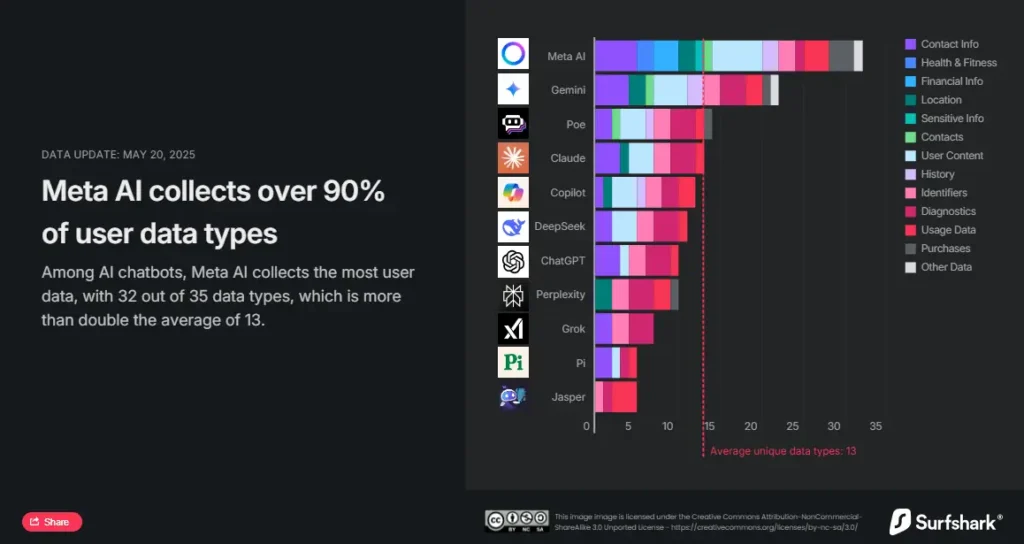
Google Gemini ranks second, collecting twenty-two types of data, including precise location, contact information, search history, and the user’s contact list. Poe, Claude, and Copilot also made it into the top five, but their appetite is noticeably smaller, ranging from twelve to fourteen types of data. Meanwhile, Poe and Copilot are among those models that can track users through device identifiers and transmit this data to brokers or use it for targeted advertising.
DeepSeek is worth noting — this Chinese model is often praised for its performance, but Surfshark highlights the risks: user data is stored on servers in China and may be transferred to China Mobile, a company under government control. Moreover, DeepSeek has already faced a leak of over a million chat history records and API keys.
ChatGPT collects ten types of data but does not track users or use third-party advertising. For those who value privacy, the model offers temporary chats with automatic deletion of information after thirty days and the option to prohibit the use of personal data for training. Other models, such as Grok, Pi, and Jasper, collect between five and seven types of data, but even they may involve information for advertising or transfer to brokers.



